More and more institutions and companies see advantages in the use of Open Data but are not sure in which way they can use this data and what they should consider, especially on the legal side. This article highlights the legal and juridical challenges that companies encounter when working with Open Data and outlines an approach for using the data properly.
What Is Open Data and Why Should Companies Use It?
Open Data is data that is published by governments, companies or other organizations and is free from restrictions such as copyrights, patent rights or other limitations. It can be fully used, analyzed, shared, and modified and is available freely. The concept of Open Data is intended to promote innovation and transparency and to support economic growth.
Using open data offers companies advantages in many different respects. Overall, by using Open Data, companies can increase their competitiveness, discover new business opportunities, and demonstrate their responsibility towards society.
For example, Open Data can help companies simplify market research and gain quicker insights into market and industry trends so that they can adapt their offerings and strategies accordingly. Open Data can also be useful in developing new products and services by giving companies insights into consumer trends and behavior. In addition, business processes can be optimized, and costs can be saved by making better decisions based on data.
From a social perspective, Open Data can help companies develop partnerships and collaborations with other organizations by giving them access to shared data resources. Companies can, as an example, share data that is relevant to solving social problems.
What Are the Legal Limits of Open Data in Germany?
However, it is important to be aware of the legal boundaries and requirements that apply to the data. While there is no single legal framework governing Open Data, several laws and regulations apply to the collection, processing, and publication of data.
In Germany, the legal boundaries of Open Data are regulated by several laws and regulations aimed at protecting privacy, data security, intellectual property, and other rights. The most important laws and regulations related to Open Data in Germany include:
- the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
- the Federal Data Protection Act (BDSG)
- the Freedom of Information Act (IFG)
The GDPR regulates the processing of personal data within the European Union (EU) and applies to all EU Member States, including Germany. It sets out the principles of data protection, including the requirement that personal data may only be processed if it is done in a lawful, fair, and transparent manner. The GDPR also grants data subjects certain rights, including the right of access, rectification, and erasure of their personal data (Figure 2). If you are interested in learning more about GDPR, check out this article.
The BDSG regulates data protection in Germany and contains specific provisions for the processing of personal data. Furthermore, it defines the role of the German Federal Commissioner for Data Protection and Freedom of Information, who is responsible for enforcing data protection laws in Germany.
The IFG regulates access to public information in Germany and aims to promote transparency and accountability in the administration. Under the IFG, citizens have the right to request access to official information held by public authorities, but with certain restrictions that impact the use of Open Data.
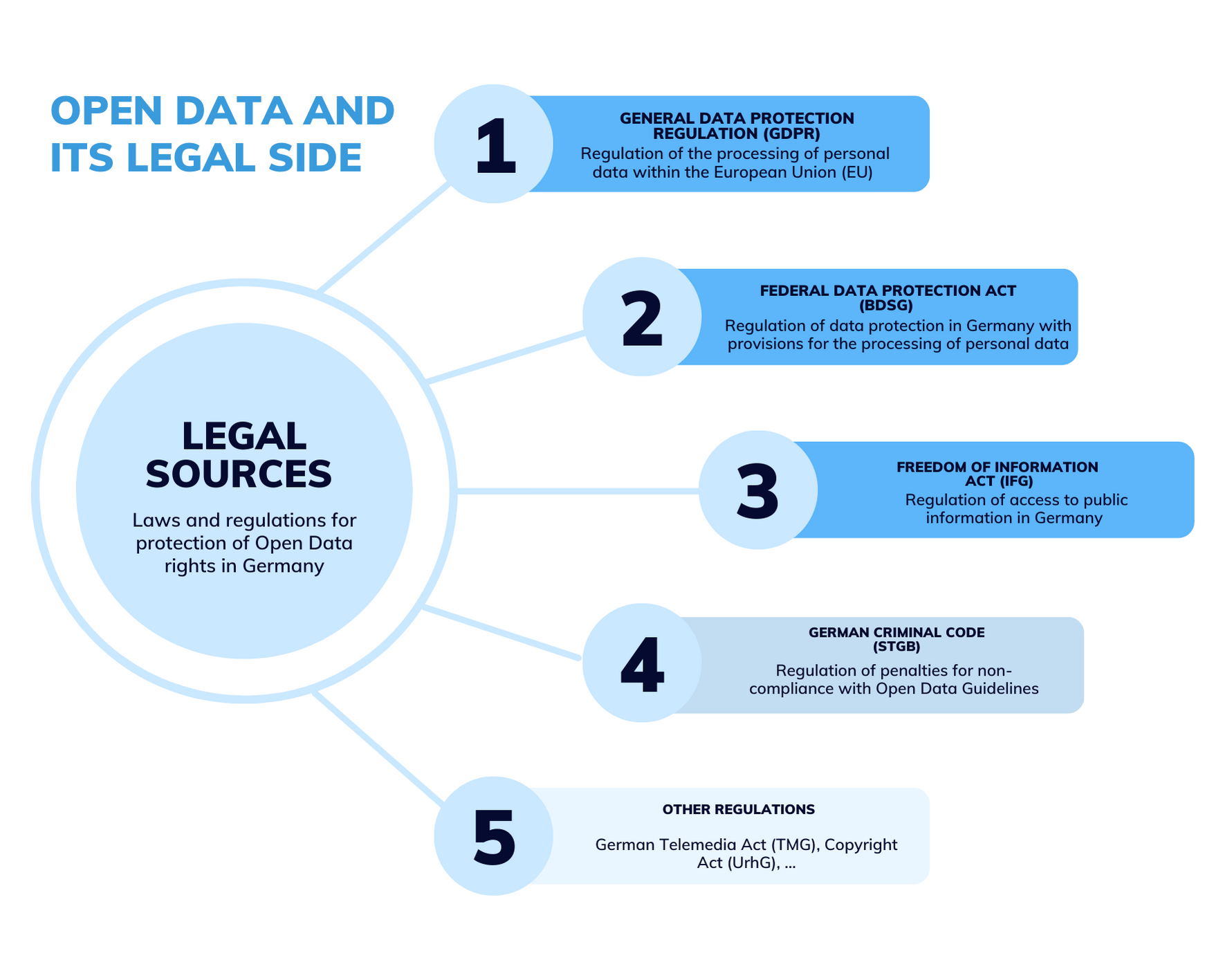
In addition to these laws, there may be other regulations that apply to certain types of data or industries. For example, the German Telemedia Act (TMG) contains provisions on the collection and processing of personal data on the internet and prohibits the publication of personal data relating to a person’s health, sexuality, or ethnic origin without their explicit consent. Furthermore, the Federal Government’s Open Data Strategy provides guidelines for the publication and use of Open Data by public bodies in Germany. And the German Copyright Act (UrhG) sets out rules for the protection of intellectual property rights, including copyright. This law can apply to data that is subject to copyright protection, such as databases and software.
These are some of the most important laws and ordinances related to Open Data in Germany. The full versions of these laws and regulations can be found online at the links below.
What Penalties Can Companies Incur if They Do Not Comply with the Legal Limits of Open Data?
Open Data refers to the release of data and information by government or private institutions to make it available to the public. The use of Open Data is basically legal as long as the terms of use and legal regulations are adhered to. However, even in the context of Open Data, various legal violations can be committed based on different legal foundations.
A possible offense is copyright infringement when data is used without the permission of the author. This is where the Copyright Act (UrhG) applies, in particular § 106 UrhG, which prohibits the unauthorized exploitation of copyrighted works. Data alteration or data manipulation can also fall under the criminal offense of data alteration pursuant to § 303a of the German Criminal Code (StGB). Another criminal offense in connection with Open Data is unauthorized data processing under § 202a of the German Criminal Code. This includes, for example, the unauthorized reading of data from a system to which there is usually no access. Spying on data can also fall under this provision. Similarly, the publication of personal data or trade secrets may violate the Data Protection Act. Violation of these conditions may constitute copyright infringement under § 106 UrhG. Furthermore, it should be noted that non-compliance with the regulations regarding personal data in the context of Open Data may result in penalties or even criminal consequences for the company. It is also a case of abuse of data under § 202c of the German Criminal Code if data is used for a purpose different than the purpose for which it was originally intended.
The exact legal basis for these criminal offenses can be found in the German Criminal Code (StGB), the German Copyright Act (UrhG), and in data protection regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which can be found in the links below.
What Should Companies Now Consider When Using Open Data?
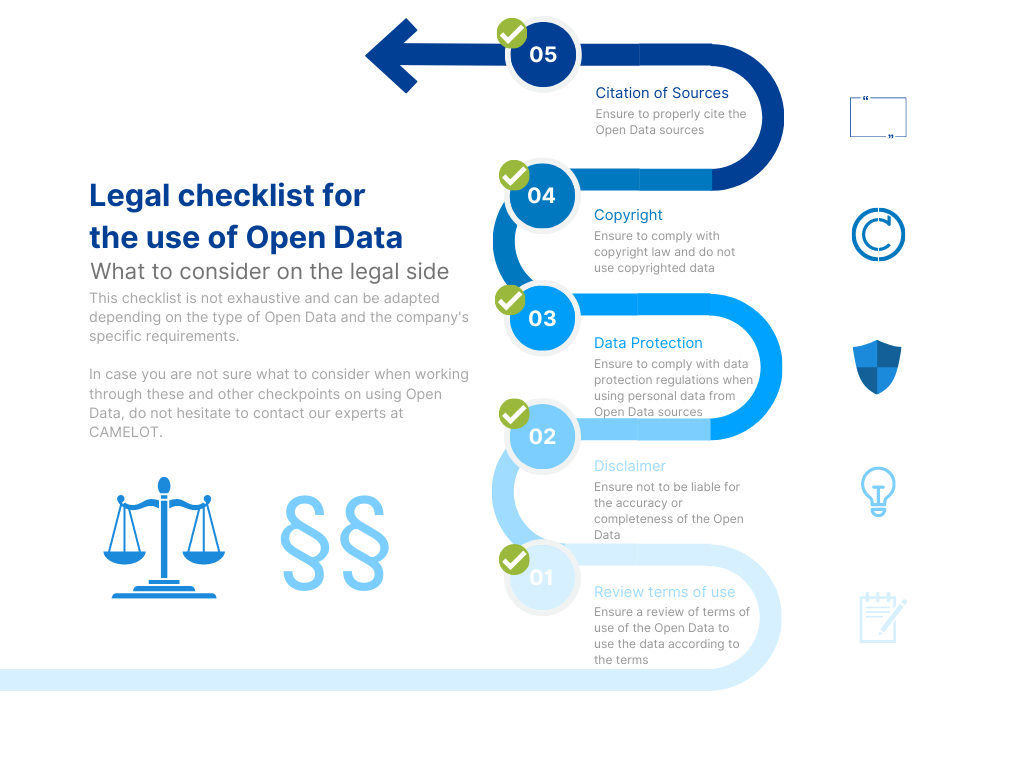
Companies that use Open Data must ensure a responsible approach to its utilization and that they comply with all relevant laws and regulations to minimize legal risks.
It is also important to verify that the data is indeed publicly available as well as freely and legally accessible. The copyrights to the data should always be respected, so that the data is only used according to the conditions under which it was published. Therefore, companies should inform themselves about the terms of use of Open Data and ensure that they comply with these terms. In some cases, it is even necessary to check whether the consent of the owners must be obtained when using the Open Data. If necessary, it could even make sense for companies to agree on appropriate limitations of liability to protect themselves from claims for damages that could arise from the use of Open Data. But also on a social level, companies should make sure that they do not engage in discriminatory practices or other unacceptable behavior when using Open Data (Figure 1).
In summary, although Open Data is encouraged in Germany, there are legal restrictions that need to be considered to guarantee that personal data and other sensitive information is protected. It is important to comply with these regulations to avoid legal liability and to protect the privacy of individuals.
I you look for advice on how to use Open Data profitably for your company or if you just have doubts whether you are complying with all the legal rules when using Open Data, please do not hesitate to contact us.
Relevant Laws and Regulations in Germany
- ACT ON THE PROMOTION OF ELECTRONIC ADMINISTRATION (EGOVG)
- GENERAL DATA PROTECTION REGULATION (GDPR)
- GERMAN FEDERAL DATA PROTECTION ACT (BDSG)
- LAW ON ACCESS TO FEDERAL INFORMATION (IFG)
- OPEN DATA PORTAL OF THE FEDERAL GOVERNMENT
- Website of the Federal Ministry of the Interior, for Building and Home Affairs

