GDPR has arrived on the agenda of most large and mid-sized companies in the EU. Consequently, companies look for tools and service offerings to support them with the adjustment of their processes to comply with the new regulations. With our long-term experience as a trusted advisor when it comes to master data, we see already that many requirements of the GDPR can be realized with the implementation of SAP Master Data Governance.
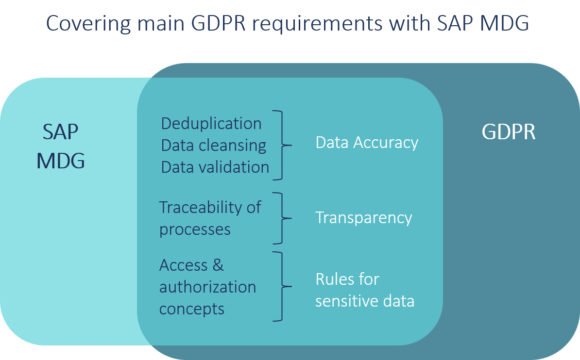
Enacted on May 25th in 2018, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) for all companies processing personal data within the European Union, has become a central topic for most large and mid-sized companies. SAP offers a variety of tools to support data protection, covering data lifecycle management (SAP Information Lifecycle Management), authorization management (SAP NetWeaver Identity Management), cyber-attack prevention (SAP Enterprise Threat Detection) and the centralized management of master data (SAP Master Data Governance). As master data is by nature created for a long period of time – permanently stored in systems and integrated into business processes – it is particularly relevant for data protection. With SAP Master Data Governance (SAP MDG) SAP offers a master data management application which can be leveraged to increase GDPR compliance on several levels. In this article, we will present how SAP MDG can be used to improve data accuracy, transparency of processes as well as the handling of sensitive data.
How to be accurate?
First, SAP MDG contributes to the principle of data accuracy by consolidating data and increasing data quality. As a tool for centralized master data governance, SAP MDG enables data consolidation by establishing one single source of truth. Out of this source, all connected systems can obtain their data and reports of data, these flows can easily be created. This approach enables the company-wide adherence of standards and rules for maintaining and changing master data. Thus, high-quality master data can be obtained which sets the basis for processes that are compliant with GDPR, transparent and at the same time efficient. Data quality in SAP MDG is ensured through different mechanisms as for instance data cleansing, deduplication and validations. As one important mechanism, validations along each and every process step ensure that only content which meets the predefined quality requirements are stored in the data record. As an additional quality gate keeper, SAP MDG provides the so-called staging area – one of the basic concepts of its central governance scenario. In the staging area all data is stored which is only partially maintained, approved or validated. Only after completion, approval and validation, data is activated and replicated to the operative systems which prevents subsequent faults in operative processes due to incomplete or qualitatively insufficient data.
Gaining full transparency
In order to meet the requirement of data transparency, the most important principle is the traceability of processes. SAP MDG supports transparency in business processes as well as in flows and changes within databases. This is done by defining and documenting a centralized maintenance process which enables to trace every change that has been made to any master data object. While this is valuable from a business perspective, GDPR requires an organizational distinction in order to prevent overarching access to explicitly locally assigned databases. SAP MDG supports this requirement by offering authorization control on the level of master data objects. Access to data objects can be differentiated for instance as follows: no access, change of data, maintenance of data, display of data, change of block and unblock flags; change of deletion flags. Thus, within SAP MDG, access and authorizations are not only transparent but more importantly centrally governed.
Sensitively handling sensitive data
The management of data access and authorizations becomes particularly important when it comes to sensitive data. An example for particularly sensitive data is employee data. Within a requirement analysis it must be evaluated to what extent authorization concepts are required. In case employees can use so-called self-services for the maintenance of bank and address data, there might be no specific authorization needed. However, in case such a concept is needed, SAP MDG offers the option to show the respective person only the necessary data while hiding all sensitive data. In this scenario, the approver would be unable to change data and would only see the information that needs to be approved. Sensitive information such as for instance marital status, date of birth or address data is then displayed encrypted.
In the end, SAP MDG is not the one tool that will guarantee to be fully compliant with GDPR. Nevertheless, it can be a key component of an organization’s strategy for GDPR compliant data handling. For any MDM projects – from pure strategy projects to MDG design and implementation projects – we therefore recommend applying the following guidelines:
- Considering GDPR requirements already in the roadmap
- Align closely with data protection officers
- Consider data protection in the roles & authorization concepts
- Ensure the fit of the SAP MDG program to the overarching data protection program and consider all parallel projects e.g. Information Lifecycle Management implementations
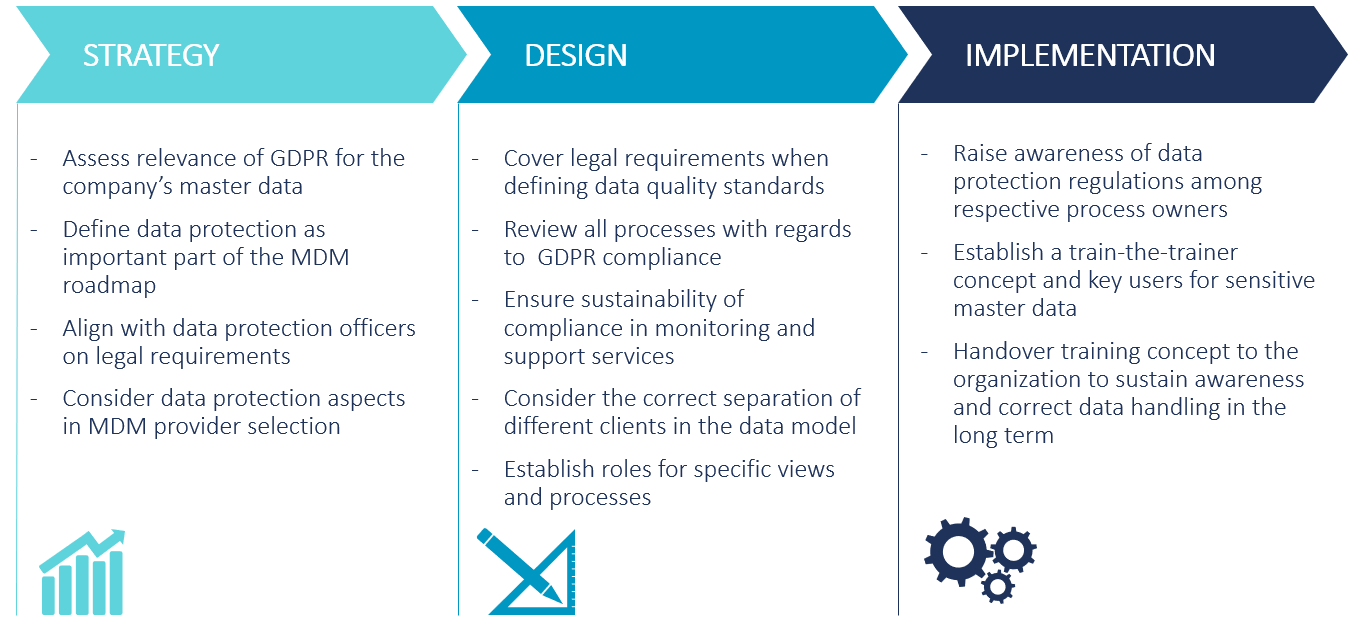
Figure 2: Data Protection as Integral Part of MDM Project Phases
We would like to thank Mirjam Baldas for her contribution to this article.