More and more technologies are producing and using large amounts of data. The sheer mass of data in enterprise infrastructures that this creates must be addressed over time. Data archiving plays an important role here and is particularly significant in the course of the transition to SAP S/4HANA. A transparent, enterprise-wide data archiving strategy is therefore part of the portfolio of data-driven companies to reduce costs, meet compliance requirements and avoid performance problems.
The amount of data managed in enterprises increased by 39% from 2018 to 2019 (vgl. Dell Inc. (2020). Global Data Protection Index – Cloud Environments see also dell-emc-proven-and-modern-ebook-.pdf). The reasons for this increase include innovative technologies such as IoT or analytics, which open up enormous potential for companies. The realization of this potential inevitably leads to even larger volumes of data and presents companies with the challenge of establishing efficient data management. In the course of ongoing digitization with increasing data volumes, companies without holistic archiving strategies will increasingly face difficulties. One driver in digitization is the transition to SAP S/4HANA as a new core application – which is either on many companies’ agendas or an ongoing project already.
Important Innovations for Companies Through SAP S/4HANA
The Simple Suite of SAP S/4HANA (‘S’ stands for simple, ‘4’ stands for the 4th generation of SAP Business Suite and ‘HANA’ stands for High performance analytic appliance) offers newly named and simplified data models through SAP S/4HANA Finance and SAP S/4HANA Logistics. Due to the simplified data structure, data points from existing systems just partly transferred; the background is that existing components are replaced by new functionalities. Data transformation therefore is a key factor in migrating existing data thoroughly. This aspect can determine over the success or failure of the transition. Thereby, it makes no difference whether it is an integration into an existing system or a completely new setup of the SAP S/4HANA system.
To make the complexity of the transition manageable in terms of data, there is a simple guiding principle: the fewer data that have to be integrated into the new system, the easier the changeover will be and the lower the risk and effort will be.
Urgency for Archiving Data
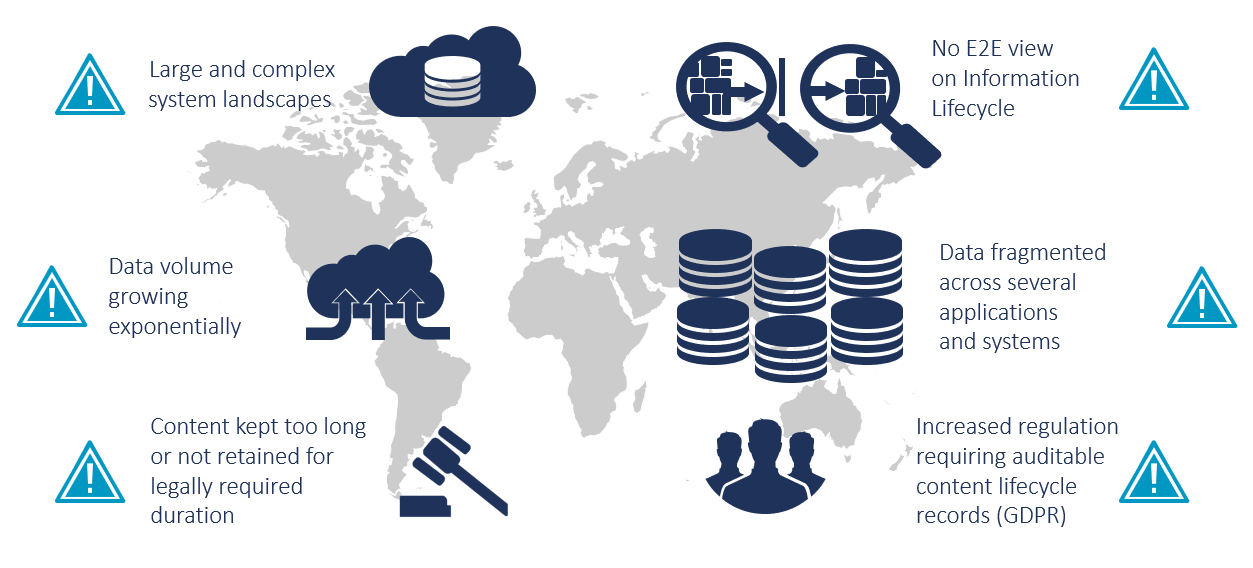
This makes archiving existing data an important preparatory step in any transition. Within large and distributed system landscapes, data grows exponentially. In this process, data becomes obsolete over time, but companies rarely delete data. In addition, companies do not have a holistic view of all information, as data silos often exist. And there are other factors that speak for the approach of archiving existing data.
1. Manage exponentially growing data volume
With the exponential growth in data volume, data management is becoming a cost factor. In addition, a lot of data in productive systems often causes performance problems. Nevertheless, data archiving is still often ignored as a solution though disadvantages that arise as a side are tolerated. The fear of potential data loss or loss of data access, as well as capacity bottlenecks in IT, which lead to the postponement of topics, and even a lack of knowledge about data archiving, become obstacles. In short, data archiving is either not on the digital agenda or is implemented inadequately, often managed with high manual effort. In addition to facilitating database handling and optimizing backup and recovery times, database reorganization can also optimize response times. As a result, system performance increases.
2. Data archiving saves immense costs
Another factor in favor of data archiving is the technical nature of the new SAP S/4HANA landscapes. Companies – as of now – often try to optimize their data management by expanding their physical storage. To do this, hardware budgets are raised, and storage capacities are increased. This solution is associated with high costs for S/4HANA in the long term: because unlike previous systems, SAP is building on an in-memory database in the S/4 core with HANA. Even if the hardware costs for in-memory databases fall, they are still three to five times higher than the costs for conventional hard disk storage. Conversely, this means that increased data volume leads to significantly increased hardware costs in the new system environment. Data archiving counteracts this by mitigating critical database sizes and addressing storage space issues. In addition, the changeover enables data to be standardized. Due to the standardized data as well as the reduced amount of data that is migrated, the costs for hardware and for the effort of the conversion to SAP S/4HANA are significantly reduced.
3. Adhere to compliance requirements (GDPR)
In addition to business aspects, tangible legal aspects, especially the GDPR requirements, speak for data archiving. The GDPR obliges companies to protect personal data and stipulates audit-proof archiving of data. Companies should therefore address this factor, irrespective of whether they are switching to a new SAP technology or not.
Strategies for Targeted and Sustainable Data Archiving
What can a holistic data archiving strategy look like that solves the challenges outlined above?
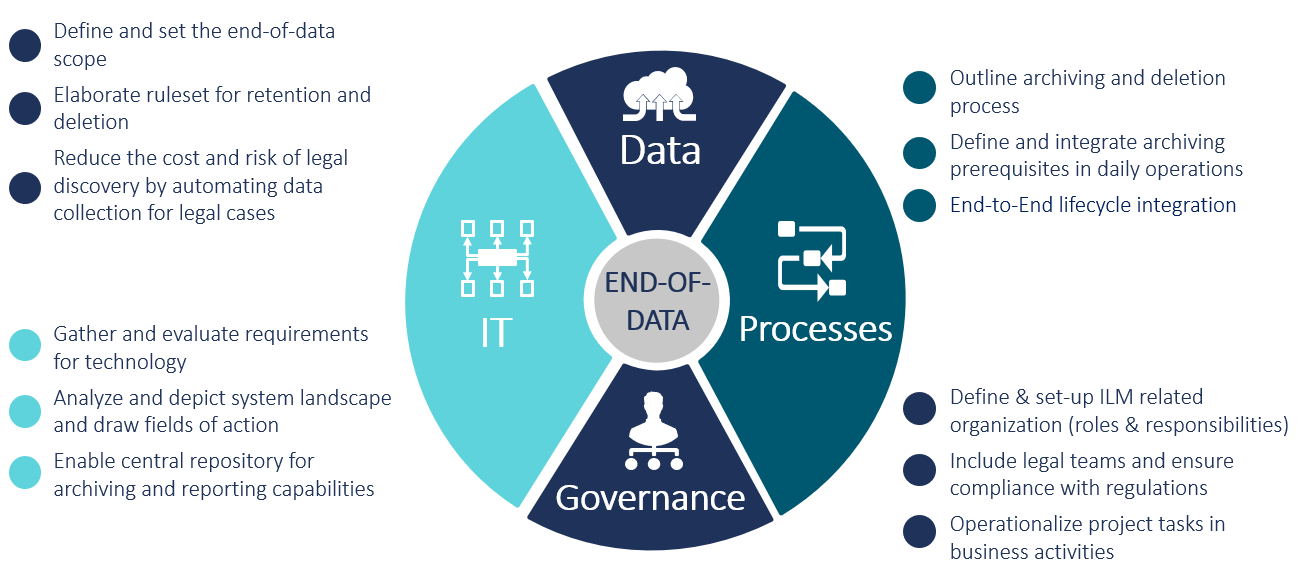
The final stages in the data lifecycle should be planned in an end-to-end approach. The CAMELOT End-of-Data approach represents such a holistic strategy and is aligned with the following four pillars:
- Data: End-of-data scope definition discusses rules for preserving and deleting data, as well as reducing costs and risks through automated data collection.
- IT: The requirements for the system technology are collected and evaluated. In addition, the system landscape is analyzed and mapped, and fields of action are derived. Using a central repository to catalog and define data quality rules, including comprehensive descriptions of rules, business aspects, and contact information, automated archiving and reporting functions are enabled.
- Processes: In the course of this end-to-end lifecycle integration, processes for archiving and deletion are outlined. Furthermore, the definition of archiving requirements and their integration into daily operations is also carried out.
- Governance: This point covers definition and establishment of information lifecycle-related roles and responsibilities. Stakeholders with legal expertise are involved to ensure compliance with regulations such as the GDPR. Project tasks are then operationalized into business activities.
Further Advantages Through an Archiving Strategy: Data Cleansing
Archiving activities are often followed by other benefits, such as data cleansing. This term describes a process that is often not yet taken into account for standardizing data and achieving higher data quality by archiving and deleting identified master data. In the course of implementing an archiving strategy and identifying data relevant for retention, transparency is created about required as well as obsolete data and thus about system resources used. Based on defined standard measures, irrelevant data can usually be removed, which can be done without additional effort during regular maintenance activities. This data carve-out is necessary anyway as a preliminary stage to S/4HANA integration and includes technical as well as business optimization aspects.
Here, a corresponding approach focuses on the validation and evaluation of master data and maintenance processes for the long-term improvement of master data quality; by considering cost aspects, the effects of inadequate data quality become apparent.
End-to-End Approach to Data Archiving
Considering numerous challenges companies face in the course of an S/4HANA transition, CAMELOT’s integrated end-to-end approach to data archiving offers an alternative to the manual data archiving still often practiced. An approach to archiving and deleting data that is individually adapted to your needs, as well as technical analysis and alignment with your system landscape, form the pillars of the end-to-end approach to data archiving. Automated management of data with defined retention and deletion rules ensures compliance with internal regulations and legal guidelines and rounds off the archiving approach.

