In the past, a profound data management strategy focusing on reducing total cost of ownership (TCO) and controlling overall data volume used to be sufficient. But as tighter retention requirements and compliance rules are emerging, the focus must be shifted towards outweighing costs with legal compliance laws and risk mitigation. Data management must be complemented by a holistic Information Lifecycle Management (ILM), especially at the last stage of the data´s lifecycle. Discover the vital benefits of CAMELOT´s ILM framework and how to close the gap at the end of the data’s life.
Why do we need ILM?
Enterprises must ensure they understand retention requirements and apply them adequately to their data strategy. Enforced by the new GDPR regulations in May 2018, the law strengthens and unifies data protection for all individuals within the EU. High sanctions (4% of annual global turnover or 20 million €, whichever is higher) drive companies to rethink their compliance and data protection strategies. Additionally, IT landscapes are growing increasingly complex and distributed. Multiple ECC’s, applications and tools are being used to create, maintain and consume data. In the digital era the volume, velocity and variety of data will furthermore increase dramatically. Companies gather and produce loads of data, but often lack to care about the end of its information lifecycle. Overall, the challenges of tighter regulatory requirements and complex IT architectures are forcing companies to rethink their data management strategy.
How ILM solves the overseen risk at the end of Information´s Lifecycle
ILM is designed to address these challenges with a combination of processes, policies, software and hardware, so that the appropriate technology shall be used for each phase of the lifecycle of the data. It acts as an end-to-end solution from data being created to data becoming obsolete and being deleted. The emphasis here, lies on the mostly unmanaged phase of archiving and deletion of data (“End-of-Data”).
Originally, data retention and the destruction of data was a manual process, that was applied to each data object individually in different systems. By defining policies for data objects stored in different places, it was impracticable to adhere and manage the deletion process efficiently. An additional effort in administration & maintenance, confusing data in reporting, as well as unnecessary storage costs are the result of obsolete, not deleted data. With ILM all your data will be centrally managed, according to your customized data retention policies. Data destruction, eDiscovery and legal holds, for audits or lawsuits, are available in one tool. By creating different archives, you can manage the lifetimes of varying data. For instance, you specify the lengths of the retention period for each object type, where the data should be retained and when it must be destroyed. These rules can be based on legal requirements (external) and/or internal compliance policies. Furthermore, ILM encompasses structured and unstructured data. A beneficial prerequisite for implementing an ILM strategy is a healthy master data management strategy & execution, reducing data quality issues in the first place.
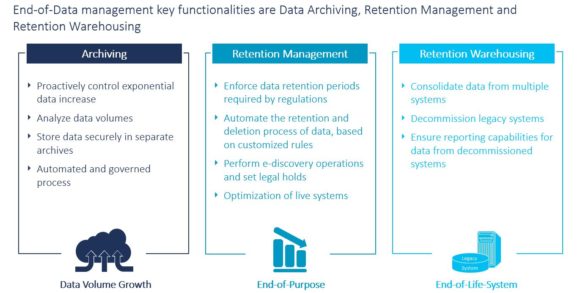
Three pillars of ILM: Archiving, Retention Management and Retention Warehousing
- Archiving is generally a standard functionality to store data on a separate archive server
- Retention Management (RM) is a best-practice solution to archive and delete different data objects due to customized retention rules
- Retention Warehousing (RW) enables the system decommissioning of legacy systems
A practical End-of-Information-Lifecycle example – Retention and deletion
Manufacturer ManuFix decides to drop business with its long-term supplier SupplyYou. Thus, SupplyYou must be blocked for future business. The transactional as well as master data, stored in multiple systems, uses valuable storage capacity and becomes a compliance risk, if not deleted within the regulatory periods. Considering the case, the manufacturer already uses a master data management tool (e.g. SAP MDG), which stores all global data (address data, contact persons, tax-, bank details, etc.) in one tool, the status ‘flag for deletion’ for the supplier can be set. The MDM tool as well as connected ECC systems will undergo an archiving run. The supplier will receive the status ‘deactivated’, but remains on the server. Regardless of the MDM tool, with ILM all data of SupplyYou will be transferred to a separate archive, based on retention rules. The final deletion of SupplyYou will be executed automatically, due to defined deletion rules; complying with regulatory requirements.
For different objects, such as invoices, tax documents, payroll declarations, contracts, etc. individual storage and deletion rules can be implemented. Let’s assume personal data needs to be deleted after 10 years. This rule can be applied with ILM and will handle the deletion process for related data. ILM automates the retention and deletion process for the End-of-Data-Lifecycle.
The 4 phases of CAMELOT´s ILM Approach
With more than 15 years expertise in the field of Enterprise Information Management, CAMELOT is the leading consultancy for mastering and implementing high quality master data management. High value and consistent master data is the first step of the digital transformation of companies. As digital frontrunner in the field of EIM, we offer an end-to-end ILM approach from strategy to implementation, ensuring that business & IT are ideally aligned and processes are well-governed.
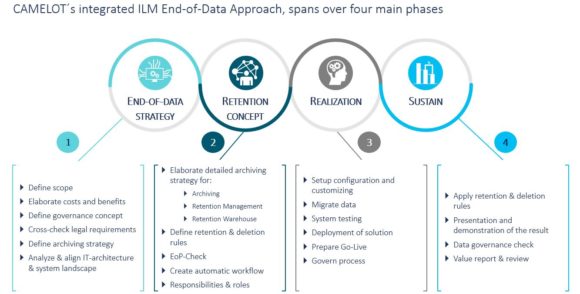
CAMELOTs holistic End-of-Information-Lifecycle approach – from strategy to implementation – Source: CAMELOT Management Consultants AG
Aligning the IT infrastructure to the business needs, including regulatory requirements and customer specific pain-points ensures a holistic management at the End-of-Data-Lifecycle. With know-how in the field of data security and protection, Camelot can help defining retention and disposal rules in accordance with data retention policy. Accordingly, we improve data quality and security as well as storage optimization. Including an efficient governance concept, ensures the process correctness at every stage
Facing several challenges at the End-of-Data-Lifecycle, CAMELOT´s End-of-Information-Lifecycle framework closes the gap of traditional, manual data archiving. By managing data with automatic retention and deletion rules, we enable internal compliance- and legal regulation policies are being obeyed. For further information on the topic of Enterprise Information Management, MDM & ILM, please reach out to us.

