Have you heard the phrase “data is the new gold”? Many companies use their data for new technological solutions and business opportunities. However, their endeavors only work with correct and resilient master data. This article highlights five reasons how bad data hinders your future business model. Our next article focusses on an approach towards solving master data issues.
During the past years, data has become the focal point of interest for many businesses: advanced analytics help to enhance business processes, data can be turned into money by selling information, and the entire business model can be tailored towards a data driven company. Buzzwords like Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) enhance the excitement of using the data available within a corporation. As soon as the C-level gives the “go” to explore data usage possibilities within the company, the newly appointed data managers quickly realize: to be able to use the available data in fancy AI solutions, a reliable, robust data basis must be established. And a first step to a meaningful data basis is securing resilient master data.
But why is correct master data so important? What happens if master data is not maintained well?
In this article, we will look at the various challenges arising from deficient master data. In subsequent articles, we will then focus on the mitigation possibilities.
Five Impacts of a Non-Resilient Data Basis
Master data is the backbone of every business process. When handling a purchase order, you need the name, the address and possibly bank details of your supplier. When creating a sales order, entering the correct name and delivery address of your client is vital. Goods receipts are only processed correctly if you have the correct dimensions of a material and its packaging. So, what happens, if this data basis is not resilient? There are several issues we have identified together with our clients.
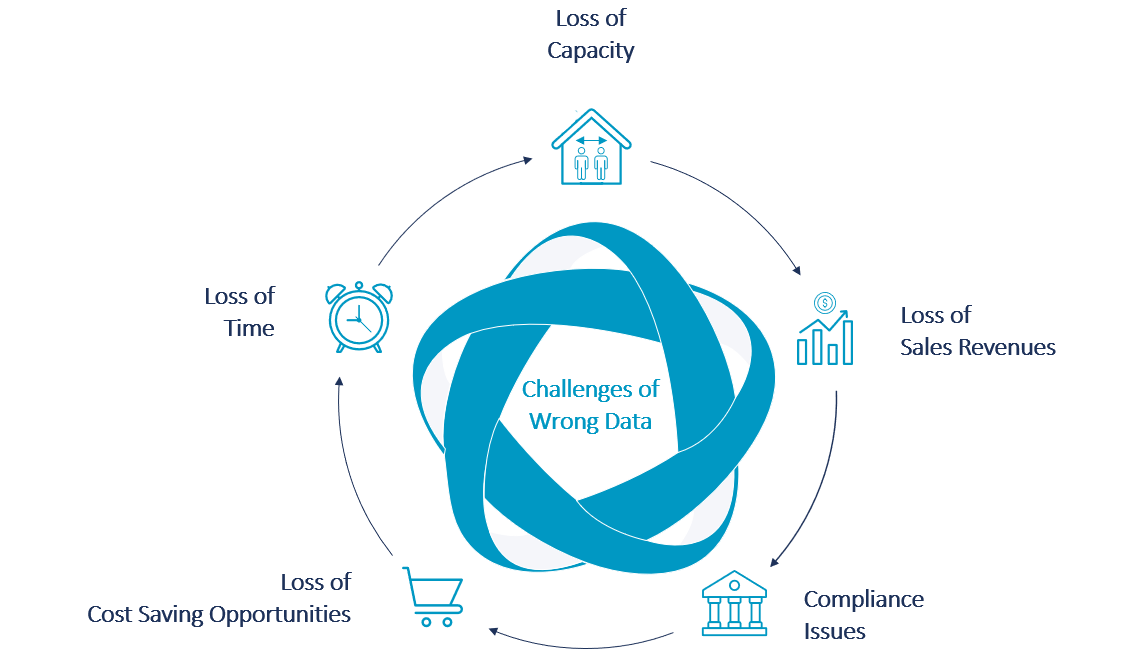
Loss of capacities
Possibly the most obvious issue, is the capacity needed to correct wrong data. As an example: A delivery arrives at a storage place. The warehouseman tries to book a goods receipt and chooses a storage location. Due to incorrect dimension data, the IT system rejects a storage location that is physically correct. The warehouseman now must manipulate data to convince his system to let him enter the chosen storage location, which reduces his overall capacities.
Loss of time
The second issue revolves around time. A customer has ordered a product from a company. The company releases the order, however, the delivery address, which is different from the customer’s headquarter, is not maintained in the system. Once the product arrives at the wrong address, the customer claims the error and time is taken to recover the wrongly delivered product and to resend it to the correct address.
Loss of sales revenues
The third issue describes the sales revenues which are missed out on. The sales department analyzes sales data to derive for example on-sale opportunities. If there are duplicates of one customer in the system as well as duplicates of the materials sold to the customers, it becomes difficult to consolidate the data at the end of the year. There is no clear picture of which material was sold how many times to a specific customer, resulting in missed sales opportunities.
Loss of cost saving opportunities
The fourth issue is the counterpart to the lost sales revenues. The purchasing department can use analytics to derive consolidation opportunities for purchased goods. High quantities can trigger negotiations with a supplier for discounts or framework contracts. However, once again duplicate master data may conceal the correlation of a product and a supplier, so that there is no reliable data base for optimization.
Compliance issues
The last issue discussed here is compliance. A short story easily pictures the difficulty. A Swiss company produces goods for a customer in France. One day, the Swiss clerk tries to release a delivery. The IT system recognizes that the delivery address is in France and asks for customs information. The clerk is not sure how to handle this and quickly changes the address of the customer to a Swiss address, triggers the delivery and once again manipulates the delivery address back to the location in France. As a result, the delivery gets stuck at customs.
The Need for a Resilient Database
As depicted, the challenges of wrong master data are manifold. A strong and reliable master data basis avoids these issues. To reach such a basis, clear master data maintenance processes and an effective governance are key. We at CAMELOT have provided the means to create the basis at many customers. We help to understand, which master data object and more in detail, which attributes, are needed for business processes. How can a company implement the meaningful maintenance processes? And what is the best practice for a governance model?
In the next article, we will detail our approach towards solving master data issues and paving the way for the hip and cool RPA, AI solutions.

