Is your warehouse ready for implementing digital innovations? There are many possibilities to prepare your warehouse for the future.
In this blog article, we want to give you an introduction how rule-mining can be used in warehousing. Other fields of application for AI in warehousing are examined in our latest thought paper.
Intelligent Rule-Mining for Warehouse Management Systems
The concept of rule-mining describes business operations, definitions and constraints that apply to an organization’s data. They reflect the business structure, serve to guide, or control organizational behavior and are put in place to help the organization achieve its goals. Or simply put, it automatically determines correlations of given business data, if a criteria A is met then a result B will be achieved (given a certain probability or confidence). Applying this to a warehouse environment can enable you to identify either internal or external dependencies. For example, if the goods are above certain morphological dimensions the picking procedure will take a certain amount of time.
Benefits for your warehouse
The advantage of this approach is to identify and compare complex enterprise rule sets against additional data sources within your warehouse database. It will allow you to understand certain interactions and behaviors. It also enables you to consider unexploited causes and optimize them accordingly. Furthermore, you can use this tool to confirm or deny correlations you assume to be true.
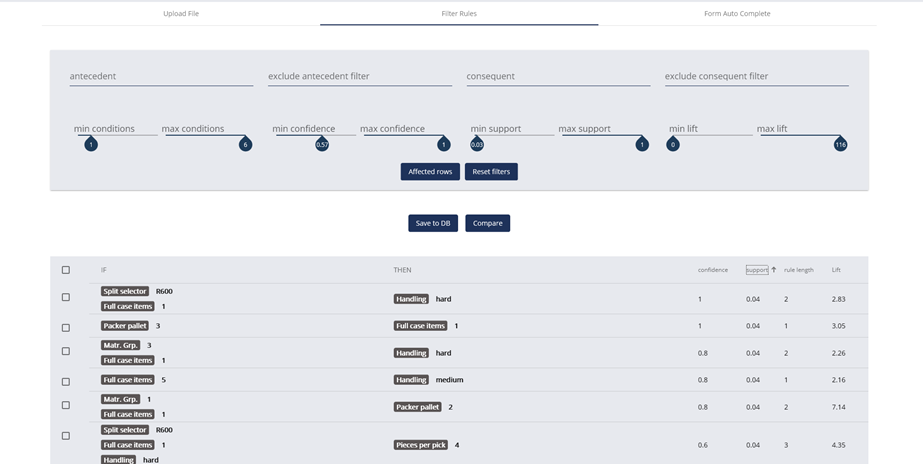
CAMELOT has developed a service offering using Rule Mining with SAP Data Intelligence. An example can be seen in the picture below:
Figure 1: Exemplary rule-mining of a warehousing data set
An additional bonus is the detection of data inconsistencies through outlier detection. The intelligent system can support the user during field value population through input suggestions and automated data population options. This subsequently enables further artificial intelligence-based innovations, since a solid and clean database is key for self-learning algorithms.
Despite the above mentioned advantages, it should be noted that the analysis is highly dependent on user input and data availability. The user needs to understand how business rules in the warehouse could reveal themselves. If an additional factor is present but not available, it will not be considered. It is mandatory to not blindly trust the system. On top of that a key accelerator is the use of parallel computing. If you prefer a rapid calculation of data, cloud-based or local computing capabilities go a long way.
Rule-mining provides a lot of context to warehousing operations and can be especially useful if you struggle to maintain an oversight. Accordingly, warehouses with a high throughput, complexity or variety of SKUs are especially suited for rule-mining. (Online) Retailers and postal service providers can additionally use this tool to evaluate and challenge their current pricing model in connection to the outcome of the analysis.
Conclusion
Rule-mining is only one of the endless possibilities of AI und subsequent innovations in warehousing. The provided example shows that at the current state of AI is still “narrow”: innovations still need guidance and/or review and cannot do multiple tasks at the same time. The concept of a “dark warehouse,” where there is no human inside a warehouse at all, is often described but still far off.
In general, that are a lot of benefits, which can be achieved: increased efficiencies, optimization of processes and resource utilization or reduced costs. But, just as described in rule-mining, the circumstances for these innovations need to be setup properly. Data is key and the collection of relevant data commences individually with each company and should be critically scrutinized in every case.
CAMELOT regularly reviewed and discussed innovations like these during joint workshops with our customers regarding their digital warehousing vision. We provide you with insights, expertise, and guidance on how and whether you should apply these innovations and if your individual circumstances are set for such efforts. If you want to know about additional ai-driven innovations or integrate innovative technologies into your digital warehouse future vision, contact us.
We would like to thank Thomas Grill and Albert Peychal-Heiling for their valuable contribution to this article.
Part 1: Artificial Intelligence in Warehousing: Data Maintenance Automation