I find the topics of Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR) and Mixed Reality (MR) – which I refer to as Extended Reality (xR) below – truly fascinating. It provides a completely different perspective on how I as a user can interact with applications and systems. Things I saw in the past in films, which back then were far off in the future for me, have now become reality. As a result, we have decided to take a closer look at the topic and experimented with it, and I would like to share my first impressions with you in a short series of blogs.
What is the difference between AR, VR and MR?
While AR relates to the enhancement of the real environment with digital information, VR provides a completely enclosed virtual environment to the user without any interaction with the real environment. Or to put it more simply: Pokémon Go vs. Playstation VR.
The difference is clear to most people up to this point, MR (mixed reality) might still be a completely new aspect for many. MR could be understood as a combination of both. And yet there’s still more to it. Because instead of simply placing digital objects statically in the real environment, it is also possible to interact with them. Still too abstract? Then take a look at this video from Microsoft.
The end devices for the current technologies are very diverse and, especially for AR, they can already be realized on simple smartphones and tablets. For VR and MR, special headsets are usually needed. There are, however, plenty of manufacturers now. The top dogs in the VR environment include Facebook with the Oculus Rift and HTC with Vive. In the MR environment, the HoloLens from Microsoft holds number one spot.
What already seems to be an established standard in the gaming sector is still rather inconspicuous in the business segment. So is xR still science fiction or is it actually science fact? We will try to answer this question below.
Are AR, VR and MR just another (fleeting) trend?
Well to put it bluntly: no! It is still often labeled as a “gimmick”, but only because the right use case has not yet been found. And this is essential to enable the enormous potential of xR to be exploited. It’s not a question of serving all applications via xR in the future. Rather, it represents an additional access point for specific process steps that are rather cumbersome to solve with current technologies. xR addresses 3 problem areas of today’s and also traditional applications at the same time:
- Blinkered View
We humans only operate what is visible on the screen, the mobile or on workstations, and we often also combine several screens together. However, our field of vision is always restricted, so that information is not immediately visible and transparent. xR uses the entire 360° field of view of the user. - Handicapped Motion
Nearly all applications are controlled by us with the mouse, although we now often also have touch and voice control. xR takes the next step and integrates further gesture controls into and, above all, with the real environment, which in turn provides new possibilities for interaction. - Limited Location
Nowadays we almost always work on a laptop at a non-personal workspace, either in the office or at home. We have a desk, with keyboard, mouse, screen, network and power connections. Pretty much exactly as it was 20 years ago, even if a direct comparison cannot really be made. Instead of physically operating an office, it could also be virtualized. A vision that isn’t new, but still needs some development.
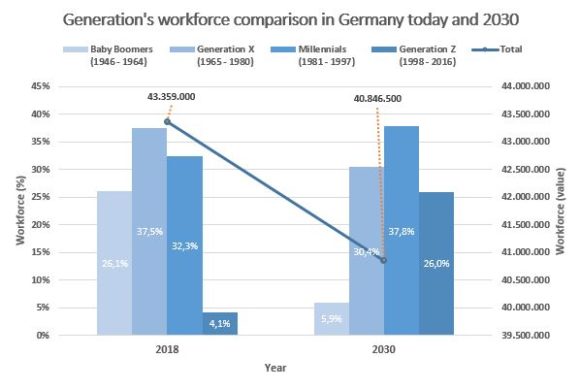
The increasing importance of xR due to the generational shift
If we also take a look at the demographic development within companies, we will see a significant generational shift in the coming years as well. Generation Z, which is used to working with digital media and technologies in their everyday lives, is entering the labor market, and they would like to see these technologies integrated into everyday working life. Baby boomers, on the other hand, are retiring and leaving the companies more and more. By 2030, the Millennials and Generation Z will account for almost 65% of a company’s employees. In other words, those generations with a digital background.
AR, VR and MR as key technologies of Generation Z
The generational shift will therefore also result in a rethinking within companies. If you want to retain existing skilled personnel and attract new skilled personnel, you must be able to provide the employees with an appropriate offer. So if, in 2030, almost 65% of employees in the future will be Millennials and Gen Z, these employees will require mobile devices, AI, IoT, xR, etc. What’s more, xR will even play a decisive role for Generation Z. The user experience is more important to them than the product itself, and xR satisfies that user experience in such a unique way that, according to Kate Harrison, this technology is crucial to retaining them as consumers.
Microsoft’s CEO, Satya Nadella, also sums it up in a similar way:
“There are three real foundation technologies which are going to shape the years and decades to come. These are Mixed Reality, Artificial Intelligence, and Quantum Computing”
“… the ultimate experience, in my mind, is what I describe as ‘mixed reality.’ The idea that you can now have both the virtual and the real world in front of your eyes and blend the two, for me, is the realization of the digital mirror being there always”
AR, VR and MR will generate enormous market volumes in the next few years
Last but not least, for those who think and act more in terms of numbers: the market volume for xR will increase almost tenfold in the next five years with a CAGR of 57%
Source: https://www.statista.com/statistics/591181/global-augmented-virtual-reality-market-size/
What is required for the development of AR, VR or MR?
In order to develop xR applications, a number of things have to be considered. In addition to a new development environment and devices, new know-how is also required. If you are already using mobile applications in your company today, no major adaptations are to be expected, at least from the point of view of infrastructure and architecture.
| Development environment | Know-how | Devices | |
| AR for iOS |
|
SWIFT |
|
| AR for Android |
|
Java, Kotlin |
|
| MR for HoloLens |
|
|
HoloLens |
| VR |
|
|
|
How can companies benefit from AR, VR and MR?
How exactly can you profit as a business? What are the possible areas of application for companies? This must be decided individually and depends on the industry in question. In general, however, it can be said that companies using xR often profit from more efficient processes, from more efficient training possibilities for their employees and an improvement in the user experience – i.e. user satisfaction and thus customer/employee loyalty. But sometimes companies find it hard to work out specific use cases, how high is the benefit or is it just a nice gimmick? So a first step here can be to obtain suggestions from outside. What is already available on the market, what have others already implemented? Let’s take a look at a few examples of how companies or industries are already using xR today.
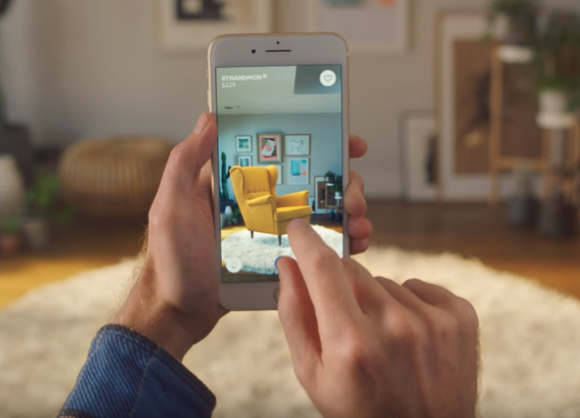
IKEA (retail):
With the IKEA Place app, IKEA offers its end customers a smart solution for integrating products from its range directly into their private environment. This means that you can virtually simulate a fully furnished living room, bedroom, etc. before you buy. This facilitates buying decisions, increases satisfaction and ultimately sales for IKEA. A similar use case can be implemented for many retail companies.
Volkswagen (automotive):
VW offers a VR experience for customers where the T-Roc can be viewed digitally in the virtual showroom. Configuration, space, technology… everything can be tested virtually before a purchase is made. This gives end customers a better feeling as to whether the configuration meets their requirements.
What’s more, Volkswagen has introduced an entire platform – the so-called “Digital Reality Hub”. It combines all VR applications used in production or logistics. Further information about this can be found in this film.
Renault (automotive):
Renault Trucks has extensively tested mixed reality technology for engine quality assurance. Employees have the possibility to display engine components virtually and to integrate virtual information and detailed steps for engine quality assurance into the field of vision. Paper-based checklists are therefore no longer necessary.
Healthcare:
In healthcare, for example, hospitals can benefit greatly from training or simulations, support during complex surgery, patient information, visits or documentation and retrieval of patient files.
Analytics:
Big Data – in visual terms, this means an area of almost infinite space, something that is difficult or only partially feasible with traditional end devices. With xR, on the other hand, this potential can be fully unleashed.
Hand gestures are standard in xR applications, AI interfaces for predictive analytics are available and can be integrated, and data points can be accessed from anywhere via the cloud. The ability to juggle data objects and perform extensive data analysis in a virtual environment is thus reality and provides a level of quality that was previously unheard of. The sheer quantity that xR can process and visualize in a Big Data environment cannot be realized with any other technology.
Conclusion
xR offers enormous potential with good use cases and can lead to significant process optimizations and more efficiency. At the moment, the difficulty is more of an organizational issue and/or related to the elaboration and identification of use cases. In the next part of this blog series, I will show you a specific use case that we at Camelot ITLab have implemented.